
At AmpLabs, we don’t treat open source as an afterthought or marketing checkbox. It is foundational to how we think, build, and contribute to the future of battery science.
We believe that scientific progress is not accelerated by secrecy—but by shared infrastructure, transparent methods, and community-aligned innovation. That’s why we invest not only in our own platform, but in the broader ecosystem of tools that empower battery researchers everywhere.
Our open source efforts aren’t about vanity GitHub stars. They’re about creating real infrastructure for the next generation of electrochemical discovery.
Every tool we build is informed by a simple conviction: that the people advancing battery technology deserve software that respects their intellect, their time, and the rigor of their work.
Whether it’s parsing obscure cycler formats or enabling high-throughput screening pipelines, our projects are designed to be not just usable—but enduringly useful.

Projects
Explore how our latest project is driving impact.
A Command Line Interface Built for the Battery Elite
Battery data deserves better than Python scripts duct-taped to CSVs. The AmpLabs CLI offers a streamlined interface to ingest, parse, and interact with battery datasets from virtually any source—locally or in the cloud.
For those who still believe in the elegance of the terminal.
The Missing Toolkit for Battery Scientists
Why should electrochemists have to reinvent the wheel for every experiment?
BatteryDataTools is a modular, opinionated Python library that offers composable utilities for battery data parsing, transformation, and visualization.
Use it standalone—or use it to make your own stack less painful.
Open source is not a zero-sum game. We actively partner with labs, institutions, and developers pushing the boundaries of battery research—and we welcome contributions, feedback, and discourse. If you’re building tools in this space, we want to know you.
The LF Energy Battery Data Alliance (BDA) was created to bring battery companies together to work jointly to unify how batteries are handled in terms of software. Battery data is core to creating a decarbonized economy and power systems, yet companies waste tremendous amounts of time implementing battery data schemas, integrations/conversions, typical calculations, etc. BDA believes that an open source tool should exist to enable researchers and engineers to focus on bringing more innovative solutions to market rather than each organization duplicating the same work.
Our Recent Work
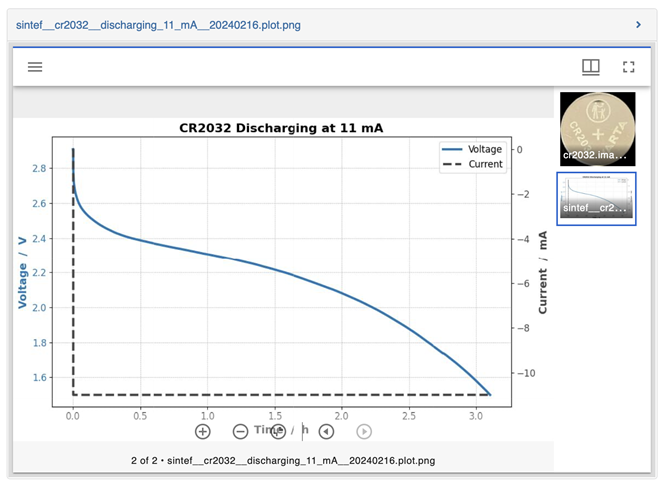
Wanted to create an agreeable format that could be plugged into Battery Ontology. As a result, we created the largest open source battery set published in the BDF format.
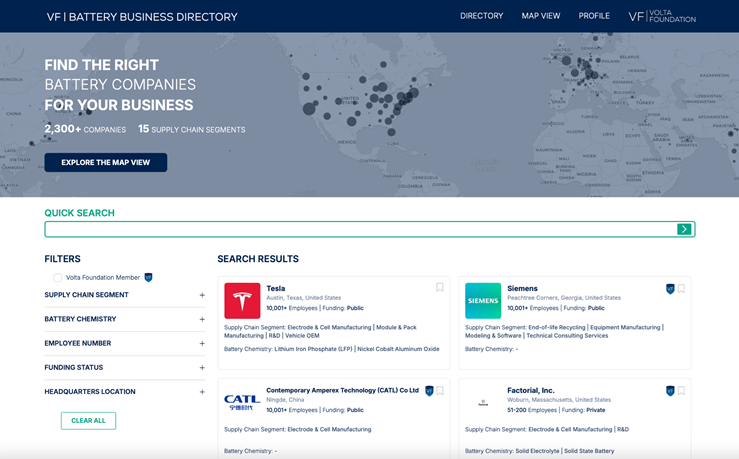
Volta Foundation wanted to make a community resource for battery information and vendors in the battery industry to help grow the battery industry ecosystem. They wanted a visually appealing interface, with admin tools, easy accessibility, and contain information about each company. The app needed to be the cornerstone of The Volta Foundation.
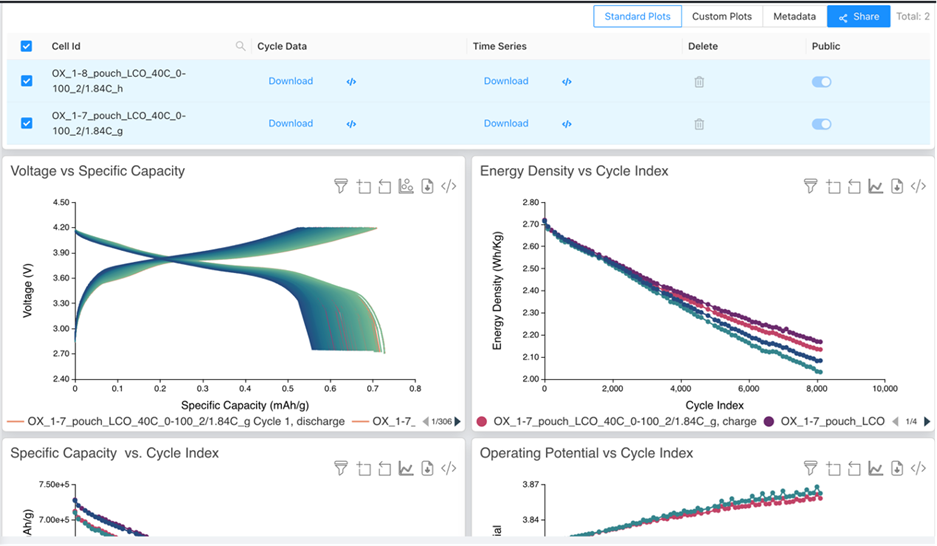
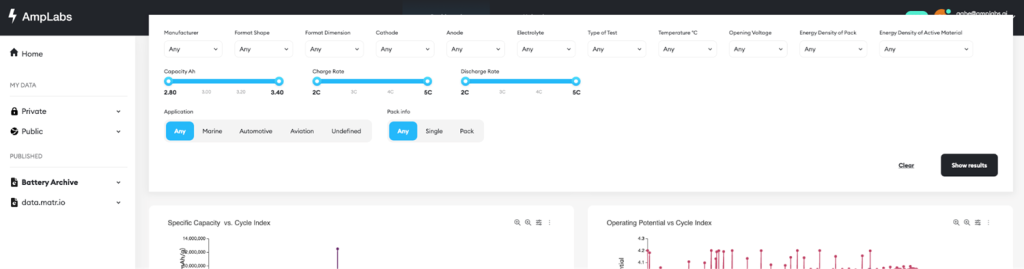
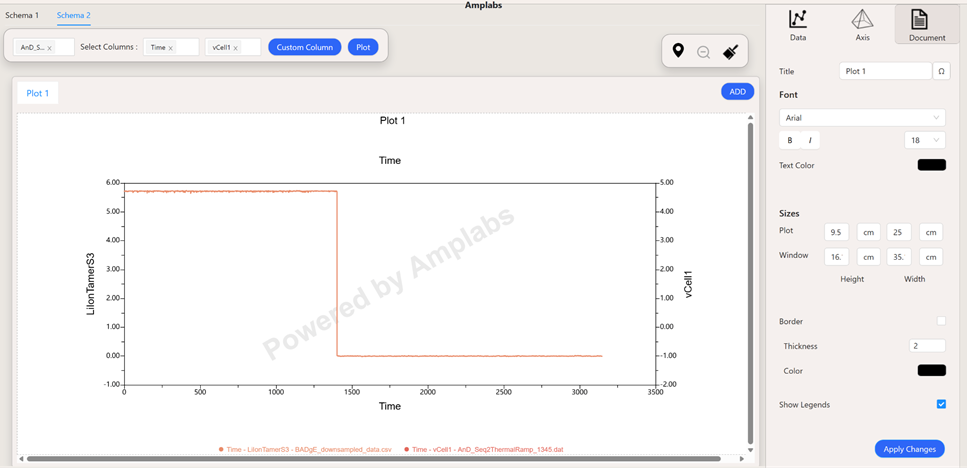
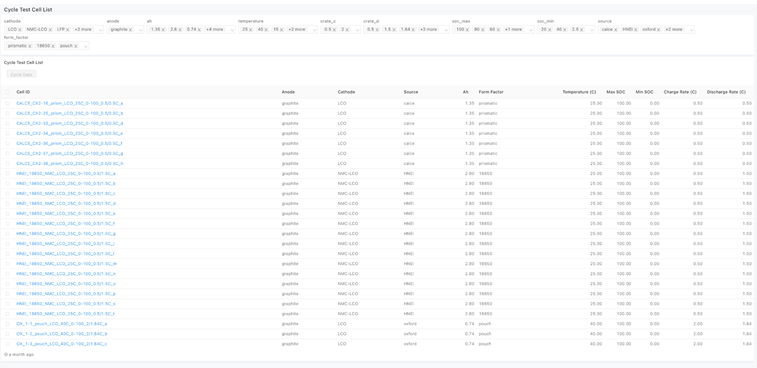
AmpLabs exists to help battery researchers move faster, think bigger, and collaborate more deeply.
Open source is how we begin that conversation—with anyone bold enough to join it.

Have an idea? A frustration? A solution worth sharing? Let us know.
We don’t just build tools. We cultivate ecosystems.
Timestamp drift refers to the misalignment of timestamps across different devices collecting battery cycler data. It poses challenges in synchronizing data sources accurately, which can significantly impact data analysis and interpretation. Understanding and correcting timestamp drift is crucial for reliable battery performance assessment.
Inconsistent units, such as mixing ampere-hours (Ah) with milliampere-hours (mAh) or watt-hours (Wh) with kilowatt-hours (kWh), can lead to inaccurate calculations and comparisons in battery cycler data. Standardizing units for capacity, energy, and temperature measurements ensures precise and meaningful analysis.
Cycle count ambiguity arises due to practices like resetting cycle counts or handling partial cycles inconsistently. This ambiguity complicates the interpretation of cycle-related metrics and can mislead conclusions about battery health and longevity if not properly addressed.
Confusion between C-rate and current often stems from misunderstandings about how C-rate is calculated relative to nominal capacity. Without accurate knowledge of the nominal capacity, interpreting the rate of charge or discharge (C-rate) versus raw current values can be misleading, affecting performance evaluations.How does missing metadata impact the analysis of battery cycler data?Missing metadata—such as details about cathode materials, anode composition, or test conditions—limits the ability to compare datasets effectively or apply machine learning techniques. Comprehensive metadata is essential for contextualizing results and enabling advanced analytics in battery research.
Managing multiple files and varying data formats during battery cycling tests creates complexity in data consolidation and analysis. This chaos necessitates standardization efforts to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and facilitate seamless interpretation of cycling performance metrics.